Author | Lucía Burbano
Is it possible to combat natural elements? Possibly not. What does seem possible, in some cases, is to mitigate the devastating effects they can cause. This Japanese infrastructure has managed to reduce the impact of an old ‘enemy’: floods that wreak havoc during the typhoon season.
Rain, a national issue
Japan has a special relationship with the rain. So much so, that its vocabulary includes dozens of terms to distinguish the level of intensity of this natural phenomenon: they use the term potsu-potsu as raindrops start falling upon the dry ground, shito-shito when it drizzles and zah-zah when it pours.
The land of the rising sun is one of the rainiest countries in the world. If the global average annual rainfall figure is 880 mm, Japan records an average of 1,718 mm. There is, however, a great difference between the typhoon season, from May to October, and the rest of the year.
Tokyo receives around 208.5 mm of rainfall in September, while in December it drops to around 39 mm.
According to estimates by Japan’s Meteorological Agency, the frequency of heavy rain exceeding five centimeters per hour has grown by 70% in the entire country. The agency blames global warming for this increase in heavy rainfall.
Damages caused by rising rivers and other bodies of water, flooding caused by torrential rain resulting in overflowing drains and sewers reached an all-time high of 2.15 billion yen in 2019.
But Tokyo is already executing a plan that is unique in the world.
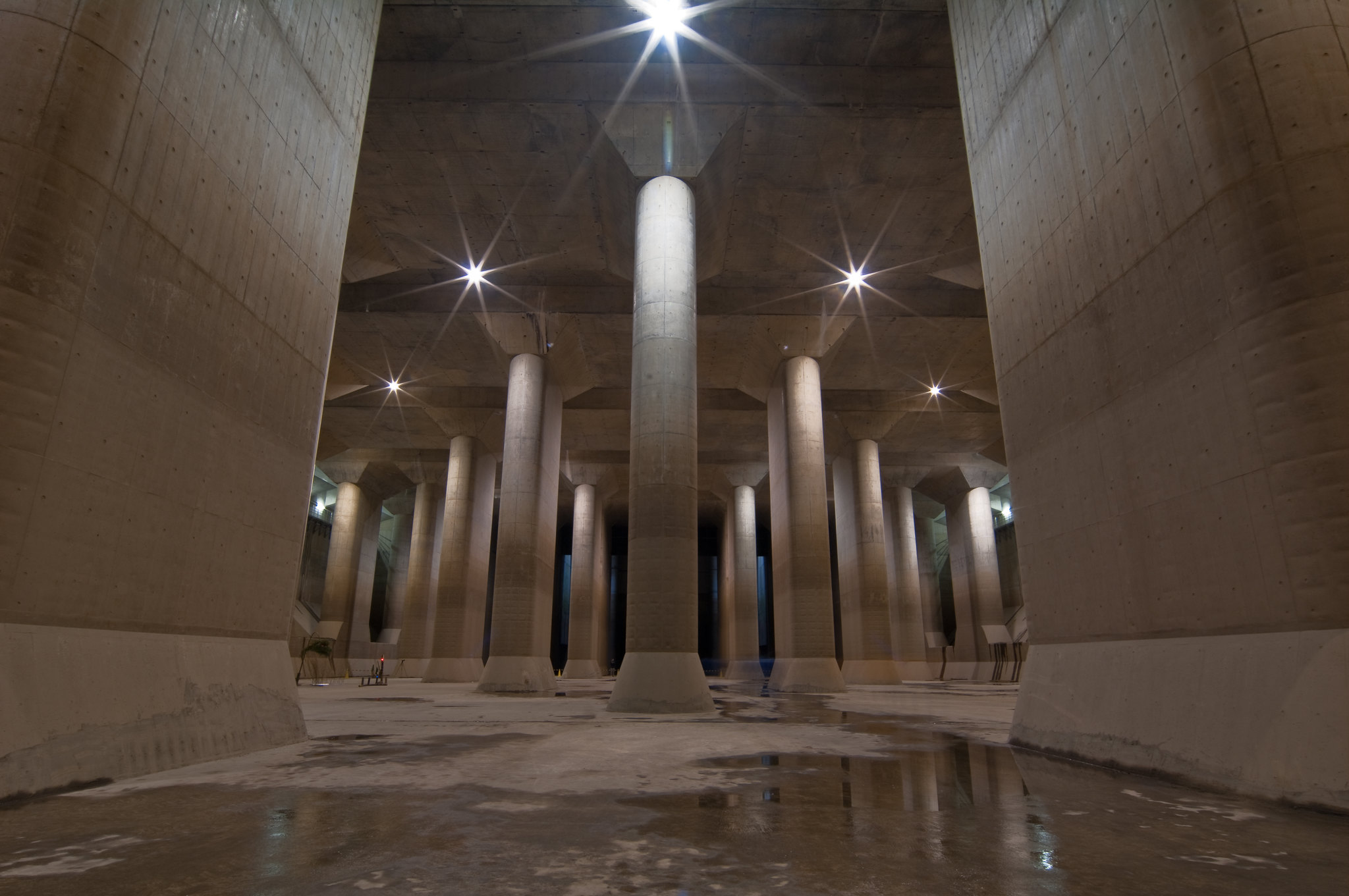
Tokyo’s underground ‘pantheon’ that manages water collection

In 1992, Tokyo began working on the Metropolitan Area Outer Underground Discharge Channel, a subterranean facility that diverts the water to the Edo River to prevent the main waterways and rivers in the city from overflowing during the rainy and typhoon seasons. It is located between Showa and Kasukabe, in the Saitama prefecture, on the outskirts of the city.
Its partial construction was completed in 2006. It consists of five concrete retention silos standing 65 meters tall and measuring 32 meters in diameter, connected by 6.4 kilometers of tunnels sitting 50 meters below the surface.
A huge water tank standing 25.4 meters tall, 177 meters long and 78 meters wide and with 59 solid pillars connected to 78 10 MW pumps are responsible for pumping up to 200 metric tons of water per second into the Edo River.
Interesting facts about the Metropolitan Area Outer Underground Discharge Channel
The cost of this mega-structure exceeded $2 billion. However, it offers numerous benefits.
- It can be visited: During the dry season, tours are organized to discover its incredible structure.
- Record figures: It is the largest underground discharge system in the world.
- One semi-Olympic swimming pool per second: The maximum drainage capacity is 200 m^3^ per second, an amount equivalent to a 25 m swimming pool full of water.
- A huge cave: Inside, it could accommodate the Statue of Liberty (46 m) or a space rocket (55 m).
- Excellent economic return for the city: In 18 years, the economic losses caused by floods have been reduced by approximately 148.4 billion yen.
- …And for its residents: Since it began, it has managed to reduce the damage caused to homes in the area by 90%.
Photographs | Flickr/Naok (CC BY-NC-SA 2.0), Kanto Regional Development Bureau