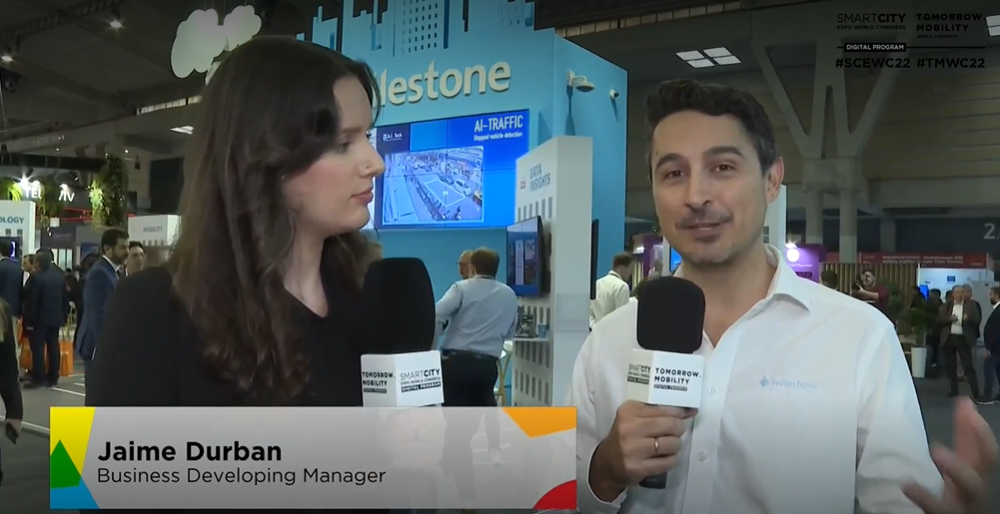
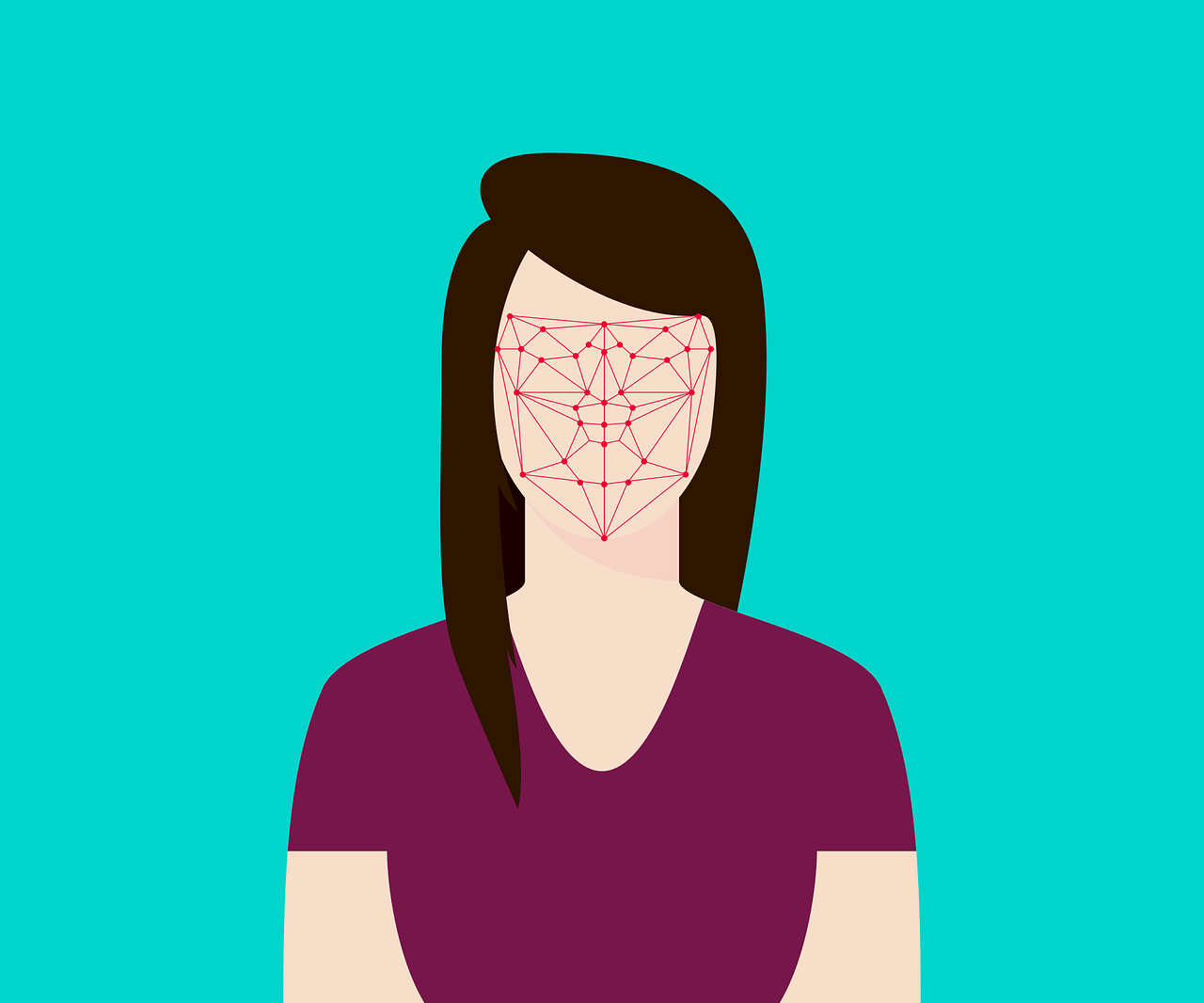
Author | Arantxa HerranzAn increasing number of cities are turning to facial recognition systems as a measure to combat crime. Moscow is one of the most recent, but before reaching the Russian capital, they could be found in cities such as Chicago or countries such as China. A measure that has had its fair share of controversy, since defenders of civic freedoms and privacy fear that technology will become a massive surveillance and, more importantly, a discriminatory weapon. Europe, in fact, is considering prohibiting the use of facial recognition systems in public spaces for five years, until measures are put in place designed, precisely, to prevent possible abuses.The problem is not so much whether this is an imperfect system (in china, for example, there is a certain degree of controversy since it was noted that at the entrance to buildings with facial recognition, people wearing masks to prevent the spread of the coronavirus are being denied access); part of the controversy is that facial recognition has significant racial, sexual and age biases.
Middle aged white men, the most recognisable
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology discovered that the facial recognition algorithms are much better with people described as white than with Afro-American or Asian people. So much so, that the errors in the identification of these people are 10 to 100 times more likely of failing than with Caucasian faces.In a database of photos used by police agencies in the United States, the highest error rates came in identifying Native Americans, according to the study. Furthermore, the algorithms had more difficulties in identifying women than men.To conduct this study, the agency tested around 200 facial recognition algorithms of around 100 developers, using four collections of photographs with over 18 million images of more than 8 million people.
Biases are maximised in artificial intelligence
The problem of biases is not new. And it is not the only one in artificial intelligence. But the main problem is that algorithms may, when badly programmed, maximise and increase these biases that affect people’s race, age, condition and sexual orientation or religion.And it not does not just affect facial recognition: a recent study also demonstrated that an algorithm widely used in hospitals in the US to assign medical care to patients has been systematically discriminating against black people.In many cases, AI can reduce the subjective interpretation of human data, since algorithms learn to only consider variables that improve their predictive accuracy, based on the training data used. Furthermore, there is significant evidence to suggest that AI models can embed human and social biases and deploy them at scale.Therefore, both humans and machines should strive to avoid biases and, with them, discrimination. Biases in AI occur mainly in data or algorithmic models, therefore the industry is looking to develop AI systems that we can trust. These systems therefore need to be trained with impartial data, developing algorithms that can be easily explained for possible analysis when false positives are identified.Images | Fauxels, teguhjatipras